
685 million people worldwide lack access to electricity. Most live in rural and other hard-to-reach areas in countries highly vulnerable to climate change. Nearly half of whom (45.5%) also live in extreme poverty and their low income hinders their resilience and ability to adapt to climate change.
Adaptation strategies prioritised by governments and climate funds often require access to energy. This goes for accessing climate information services, including early warning systems, to making livelihoods and critical services more resilient. These strategies are less feasible in off-grid or weak-grid settings in countries vulnerable to climate change, where access to electricity is limited. Off-grid solar technologies can help to address this.
Off-grid solar products, including solar energy kits, are the least cost option for providing first-time electricity access and can enhance resilience and adaptation for hard-to-reach communities in a variety of ways. This includes supporting people to access critical services (such as healthcare and water), improve their livelihoods, and access critical information (such as climate projections and early warning messages) to respond and adapt to climate hazards such as floods and drought. Following climate-related disasters, off-grid solar technologies can aid post disaster response and recovery by powering humanitarian assistance and provide energy services for displaced people.
Until now, there has been little recognition of the ability for off-grid solar to power climate adaptation. So, together with GOGLA, in partnership with Efficiency for Access and funded by the IKEA Foundation, we are launching two key resources to help stakeholders–including off-grid solar companies, NGOs, donors and impact investors–better understand and, most importantly, deliver access to off-grid solar technologies to intentionally enhance climate resilience and adaptation:
- Off-Grid Solar Resilience and Adaptation Framework: an Excel measurement tool including general instructions, use cases, and:
- A measurement resource: A compendium of measurement indicators and guidance to help stakeholders better understand, measure and evaluate the contribution of off-grid solar technologies to resilience and adaptation
- A global dashboard: A set of framing indicators that can be used by sector bodies and custodians of adaptation monitoring frameworks and indicators to track contributions made by off-grid solar technologies to resilience and adaptation at regional, national or international levels
- Sector Guidance: guidance to help stakeholders to design and implement off-grid solar business models, projects and other interventions more intentionally to enhance climate resilience and adaptation.
By encouraging stakeholders to use these resources, we aim to improve resilience and adaptation for climate vulnerable communities.
Impacts
The Off-Grid Solar: Powering Climate Resilience report and accompanying resources explore the contribution of off-grid solar technologies to resilience and adaptation across four key impact areas aligned with the adaptation priorities of governments and climate funds.
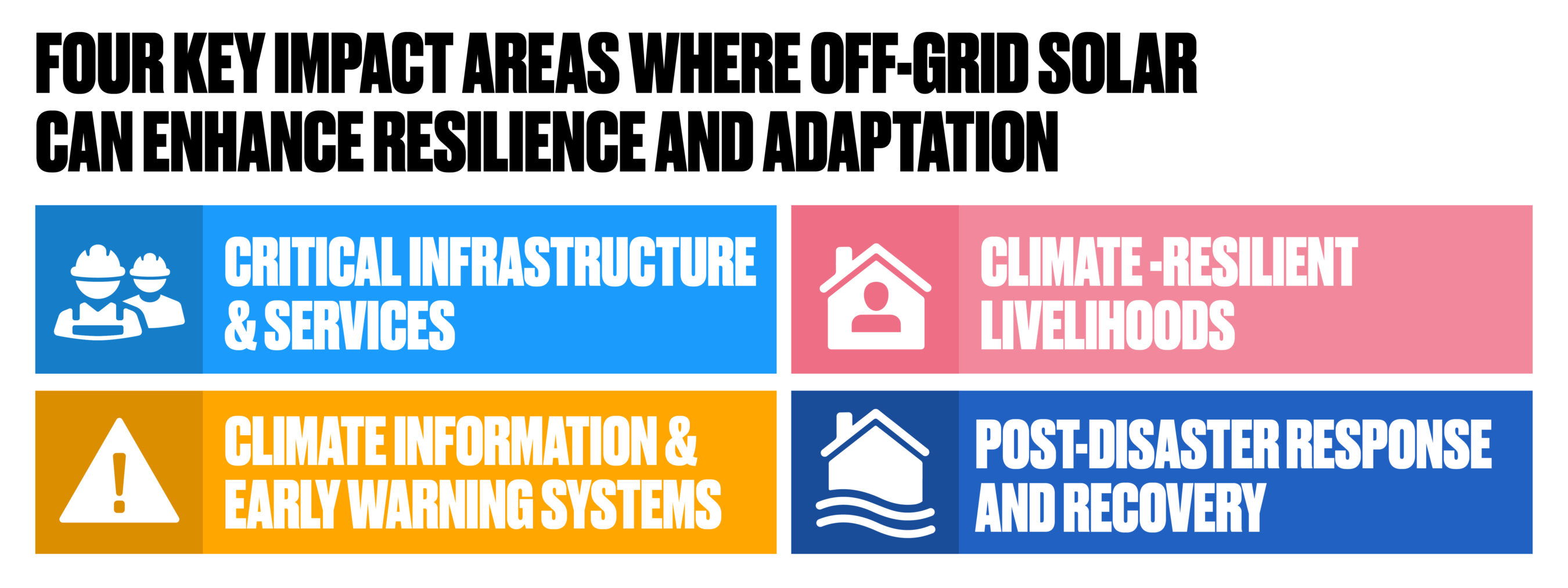
1. Critical infrastructure and services
The contribution off-grid solar makes to enhancing the resilience of facilities that provide access to vital supplies and services such as health, education, food, water, and energy access.
2. Climate resilient livelihoods
How off-grid solar can boost resilient livelihoods with things like lighting, communication, water pumps, fridges, and agricultural processing equipment by increasing incomes, jobs, savings, financial inclusion and food security.
3. Climate information and early warning systems
The role off-grid solar products and appliances in enabling and improving access to climate information services, including early warning. These are vital to helping people to take anticipatory action to avoid or reduce loss and damage.
4. Post disaster response and recovery
The off-grid solar technologies used by humanitarian agencies and displaced people in the immediate aftermath of climate disasters, including emergency response, and in prolonged displacement; helping affected communities build-back better and adapt going forwards.

Case Study
One of our recent projects–Renewable Energy for Agricultural Livelihoods in Burkina Faso—has been operating in a region where communities are struggling to adapt to climate change impacts including more unpredictable rainfall.
Now, more than 7,000 people can now use water from solar pumps to sustainably increase crop yields, create energy from biodigesters and use communal stoves and a solar refrigeration system to process food and stop it from deteriorating.
The president of the cooperative we worked with, Habibou shared how Practical Action’s support and the introduction of solar energy have transformed their lives: “Before the support of Practical Action, we faced significant challenges, particularly a lack of water, which restricted our production. Today, we have constant access to water for our crops, and this has revolutionised our productivity. We have been able to diversify our crops to meet the needs of local households, with several production cycles each year. As a result, members’ incomes have increased significantly. We can now proudly contribute to our families’ expenses and our children’s education.”
Our work shows that with the right approach and by combining modern, renewable energy with good agricultural practices, it is possible to increase production, improve farmers’ incomes and provide people with the food they need.
What next?
In the accompanying ‘Off-Grid Solar: Powering Climate Resilience’ report we call on climate funds, governments and other influential stakeholders to recognise the role that off-grid solar solutions can play in enhancing climate resilience and adaptation.
To enhance the contribution of off-grid solar products, we call for donors and investors to increase adaptation finance, and channel more funding to the off-grid solar sector.
We also recommend that the off-grid sector continues to build cross-sector partnerships with those in adjacent sectors, such as healthcare and digital connectivity, to ‘link and layer’ business models and interventions that increase resilience and adaptation.
Finally, we invite stakeholders in the off-grid solar, adaptation and related sectors to use the resources accompanying this report to improve outcomes for climate vulnerable communities.
The framework, associated guidance and report will be launched today during the Sustainable Energy for All Global Forum.
Initially, the framework and guidance will be released as beta versions allowing off-grid solar companies and other stakeholders to apply the tools in real-world scenarios. Practical Action will then work with GOGLA to update and refine the resources in early 2026, based on their feedback.
Mattia Vianello, Head of Energy at Practical Action, said, “These resources are invaluable for strengthening climate resilience and adaptation as the challenges intensify. Building on our cross-cutting expertise and learning, we’ll deepen our impact by bringing together the right partners and influencing policies to expand energy access, reduce disaster risks, enhance adaptation, improve agricultural livelihoods, and support more inclusive, resilient communities.”
The reports and associated tools are available here: Resilience & Adaptation – GOGLA